What is OP_VAULT?
OP_VAULT is a feature that adds extra security to Bitcoin, helping protect it from theft or unauthorized access.
The decentralized nature of Bitcoin has revolutionized the digital economy. Still, as its use grows, so does the need for enhanced security. This is where OP_VAULT comes in, an innovative feature introducing a mechanism called “covenants” to offer added security and flexibility.
In Bitcoin, “OP” stands for “operation code” or “opcode.” OpCodes are part of Bitcoin’s scripting language and represent individual commands or instructions that tell the blockchain what to do with a transaction. These codes enable Bitcoin scripts to add functionality and enforce rules. For example, OP_CHECKSIG verifies digital signatures, while OP_RETURN enables embedding data on the blockchain. The “OP_” prefix is standard for these commands, making identifying them quickly within scripts easy.
But what is a covenant in Bitcoin?
A covenant in Bitcoin is a rule or condition that dictates how funds can be spent. Beyond a standard one-time authorization to spend coins, a covenant adds ongoing constraints, creating a structure where specific actions must be followed even across multiple transactions. This means that covenants can ensure a coin remains protected by certain rules over time, enhancing security and enabling unique spending conditions.
So, where does the vault fit in here?
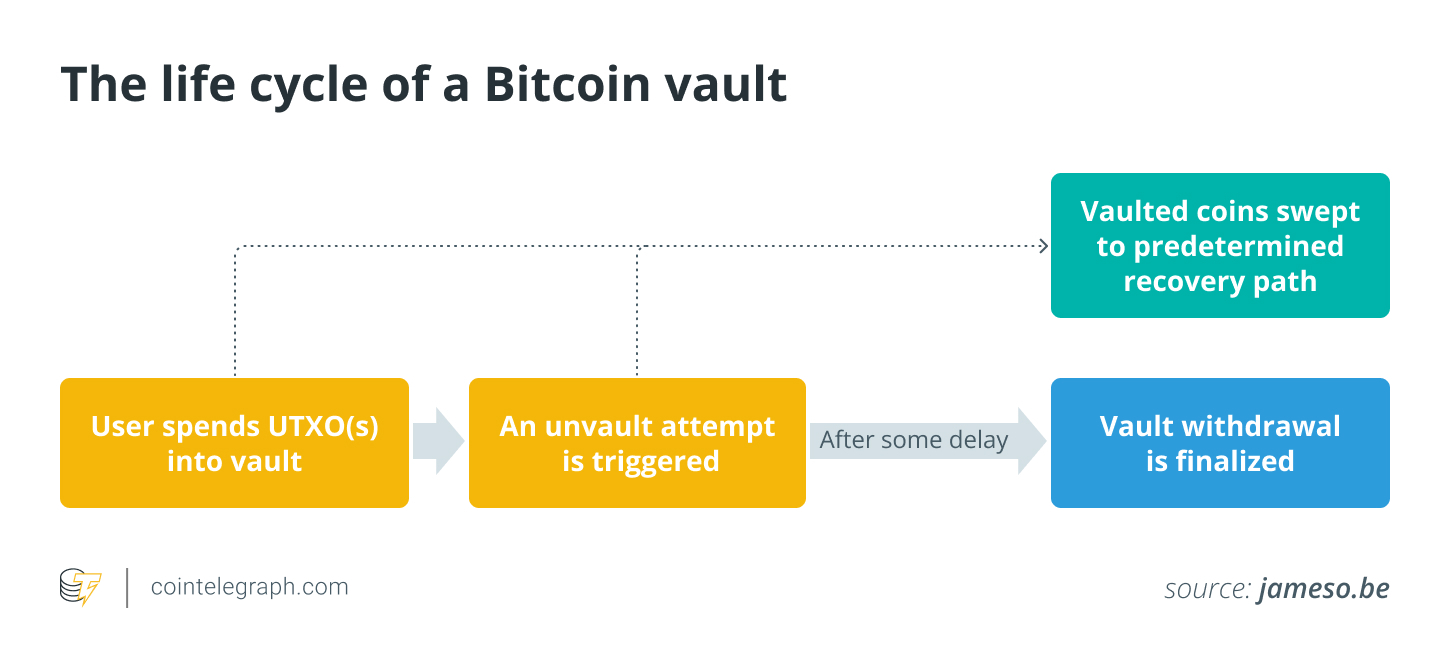
Vaults are a practical form of covenants that focus on simplifying everyday use while adding extra safeguards against unauthorized spending.
Here’s how vaults work:
- Setting up a vault: To secure funds, a user places them into a vault and sets up a monitoring process (like a “watchtower”) to observe the blockchain.
- Unvaulting process: If an attempt to withdraw funds (called “unvaulting”) is made, it goes into a waiting period, which gives the vault owner time to respond.
- Clawback mechanism: If an unvaulting request is unexpected, the owner can initiate a “clawback” to pull funds back into a secure account, preventing unauthorized spending. A clawback is a security mechanism that allows users to reclaim or “clawback” funds if they are in danger of unauthorized spending.
Did you know? In Bitcoin, a watchtower is a monitoring system designed to help protect users’ funds, especially in cases where advanced features like vaults or payment channels (such as those used in the Lightning Network) are involved. Watchtowers constantly monitor the blockchain for any suspicious or unauthorized activity involving a user’s funds and can take action if such activity is detected.
Who introduced OP_VAULT and its development through BIPs
OP_VAULT is part of a broader trend in Bitcoin to introduce more advanced features through Bitcoin improvement proposals (BIPs), formal documents used to propose changes or improvements to the Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin developer and researcher James O’Beirne proposed OP_Vault in 2023, detailed in BIP 345. This proposal aimed to create a structured approach for securely storing Bitcoin using vaults. O’Beirne’s work on OP_Vault builds on earlier advancements, such as OP_CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY (CTV), and has been instrumental in shaping Bitcoin’s covenant framework.
Notably, BIP-119, introduced by Jeremy Rubin (Bitcoin developer, researcher and advocate), brought in OP_CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY, which laid the groundwork for OP_Vault by allowing secure vault structures without the need for complex key management.
How does OP_Vault work?
Features like OP_CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY (CTV) make it possible to use vaults without requiring complex setups, such as storing presigned transactions or managing temporary keys.
With CTV, the vault’s conditions and potential transactions are precomputed and “locked in” on the blockchain, making it straightforward to monitor and manage funds without additional storage of sensitive data. This greatly reduces risks tied to losing critical information or operational complexity.
Key components of an OP_Vault
An OP_Vault setup has three essential elements:
- Recovery path: This is a backup address where funds can be directed if needed, usually secured with stringent conditions like offline or multisignature wallets. All vaults sharing the same recovery path can be batch-managed, which is useful when handling multiple vaults.
- Unvault key: This key allows the process of unvaulting (attempting to spend from the vault) to start. Still, even if an attacker gains access to this key, they can’t immediately steal the funds, as the unvaulting can be stopped and redirected to the recovery address if detected in time.
- Unvault target: This is where the funds are ultimately meant to go after the unvaulting delay. The target is flexible and can include various destinations (including amounts), enabling setups like partial unvaults or even creating new vaults.
How to use a Bitcoin vault
Create a vault to securely store Bitcoin, deposit funds, set recovery options and use a watchtower for monitoring; if needed, trigger a clawback to recover funds and keep them safe.
- Create a vault: Use a wallet or service that supports Bitcoin vaults to create a vault address configured with a covenant. This is where your Bitcoin (BTC) will be securely stored.
- Deposit Bitcoin into the Vault: Send your Bitcoin to the vault address, similar to sending Bitcoin to a regular wallet address. The vault ensures extra security through specialized rules.
- Set recovery and security options: Choose a recovery address (a secure backup location) for your Bitcoin. This could be an offline wallet or a multisignature setup for extra protection. Optionally, configure a watchtower to monitor your vault for unauthorized access attempts.
- Withdraw from the vault: To access your funds, you must go through an unvaulting process, which typically involves a delay to ensure security and allow time for intervention if necessary.

If something goes wrong and you need to recover your Bitcoin from the vault, the process is simple but requires a few extra steps:
- Detect unauthorized activity: Watchtower or you notice if someone tries to access your Bitcoin without permission.
- Trigger clawback: Use the clawback feature to send funds to a secure recovery address. The watchtower can automatically do this for you, or you can do it manually by using your wallet or service to broadcast the clawback transaction.
- Bitcoin is safe again: The funds are moved to your recovery address once clawback is triggered, ensuring they stay protected.

Benefits and limitations of OP_Vault
OP_Vault benefits Bitcoin security by simplifying key storage and enabling batch recovery management, though it limits flexibility with fixed destinations and lacks batch unvaulting capabilities.
The OP_Vault approach offers several advantages for Bitcoin security:
- No need for complex key storage: It reduces dependency on temporary keys and extensive transaction storage, as CTV handles most of the work.
- Efficient fund management: It enables batch operations for recovery, making it easier to manage multiple vaults simultaneously.
- Defending against 51% attacks: Despite Bitcoin’s robust network, high-value holders (whales) remain susceptible to social engineering and targeted attacks. OP_VAULT aims to enhance security by introducing multi-signature requirements or other complex conditions, making it significantly harder for malicious actors to access funds.
However, OP_Vault also has limitations:
- Fixed destinations: Once the destinations are set, they cannot be changed, which can restrict flexibility.
- Fungibility concerns: Bitcoin in vaults, especially with advanced features like OP_VAULT, might lose fungibility if linked to suspicious transactions or blacklisted addresses. This can diminish the value and liquidity of specific coins, as they may be rejected by exchanges or other participants.
- No batch unvaulting: It does not currently support combined unvaulting, which can limit response options in high-risk situations.
- Physical attacks: Physical theft of hardware wallets or other key storage devices linked to Bitcoin vaults can result in the loss of access to funds.
When will OP_VAULT be implemented on Bitcoin?
The timeline for OP_VAULT’s implementation depends on the progress of related BIPs, particularly BIP-119, which introduces the concept of covenants with OP_CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY (CTV).
OP_VAULT is still in the proposal stage, and there is no official release date. Bitcoin’’s development process is conservative, and changes undergo rigorous testing, peer review and community consensus.
To further improve the security of user funds, future updates may include extra features like location-based transaction limits, biometric access or even AI-driven monitoring for questionable activities.
If OP_VAULT gains broad approval, it may be included in future Bitcoin upgrades, but this may take months or years, as the Bitcoin network prioritizes stability and security. Therefore, users should monitor the development closely for updates.